



Dust was long considered the bane of astronomers, blocking off light and hiding away objects they wanted to observe. But with the advent of infrared astronomy, researchers found that dust is not a dull curtain, but rather an active and essential ingredient for the way that galaxies evolve.
In recent decades astronomers have come to see dust as a source of scientific discovery and, as demonstrated by a set of images recently released by Hubble scientists, it can be strikingly beautiful as well.

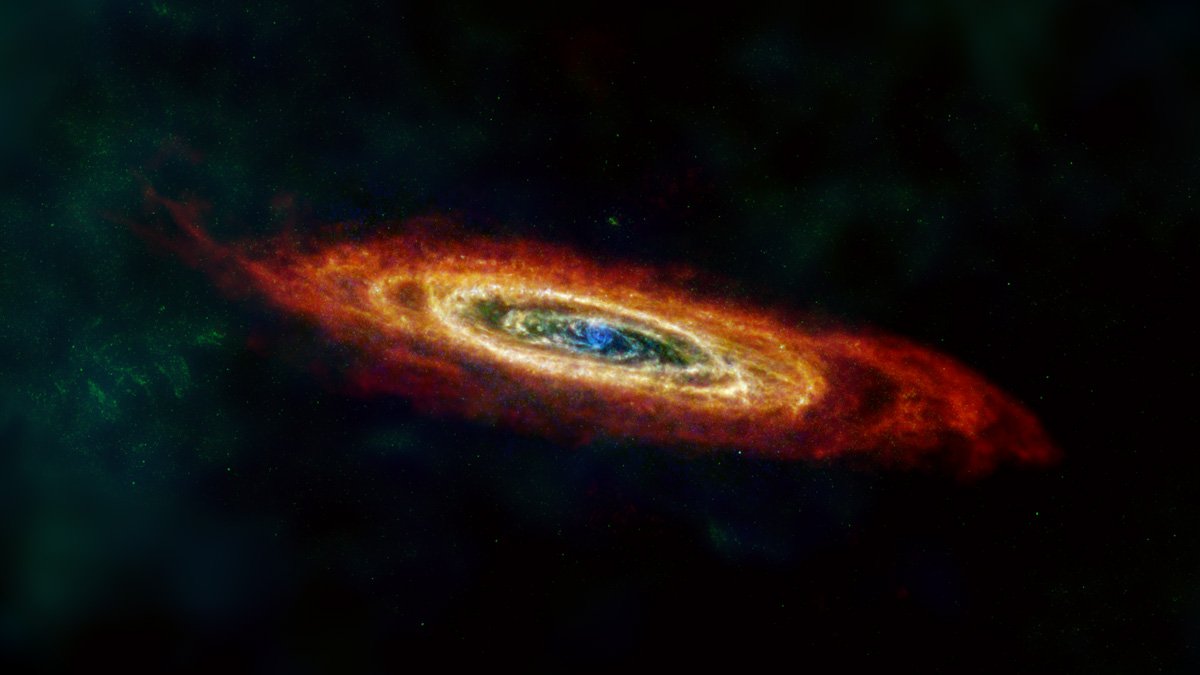
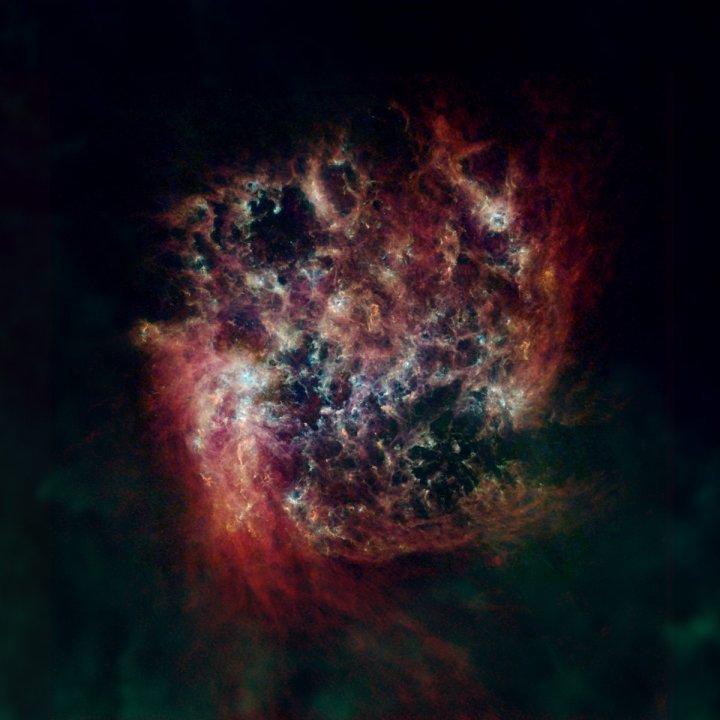
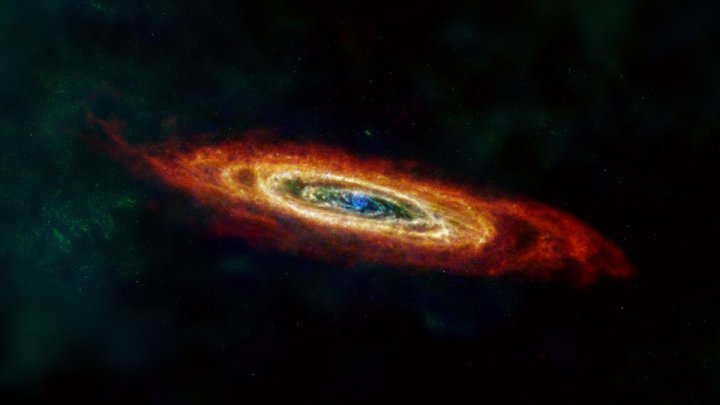
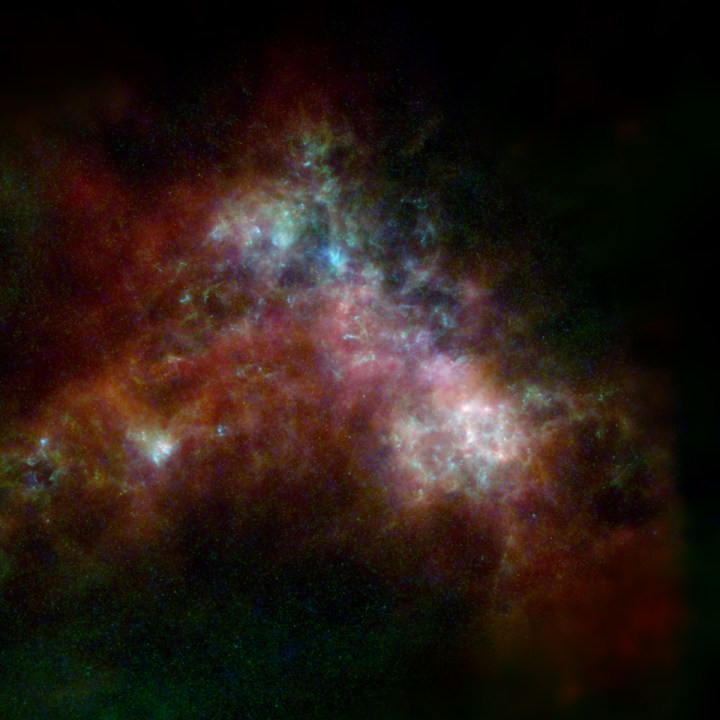
Researchers have used data from four telescopes no longer operating — the European Space Agency’s Herschel Space Observatory and Planck observatory, and NASA’s the Infrared Astronomical Satellite and Cosmic Background Explorer — to create images of four nearby galaxies to the Milky Way. The images show the dust in and around these galaxies in all its glory, color-coded to show cool dust in green and warm dust in blue, with hydrogen gas in red.

The four galaxies pictured are the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds (two dwarf galaxies orbiting the Milky Way), plus the nearby Andromeda and Triangulum galaxies. The images show how the density of dust varies within these galaxies, as it is thrown off by exploding stars and blown around by stellar winds.

“These improved Herschel images show us that the dust ‘ecosystems’ in these galaxies are very dynamic,” said Christopher Clark of the Space Science Telescope Institute who led the work to create the new images.
For example, dust is crucial to the formation of new stars, so researchers can spot areas where stars are being born by looking for empty bubbles within the dust.



No comments:
Post a Comment